NJU Static Analysis - Introduction
程序分析这块还处于宝宝阶段,故做下课堂笔记
感谢李老师和谭老师的开源精神~~ :)
(笔记中的截图来自于两位老师的PPT)
Why?
程序可靠性
空指针、内存泄露
程序安全性
检测注入攻击路径
编译优化
死代码优化、代码移动优化
程序理解
程序调用关系、类型检测
What?
Static Analysis
给定程序P,在不运行P的情况下,使用静态分析程序对其分析,判断P是否满足特性Q
Rice Theorem
=> No Perfect static analysis
Perfect Static Analysis
Sound and Complete => Perfect Static Analysis
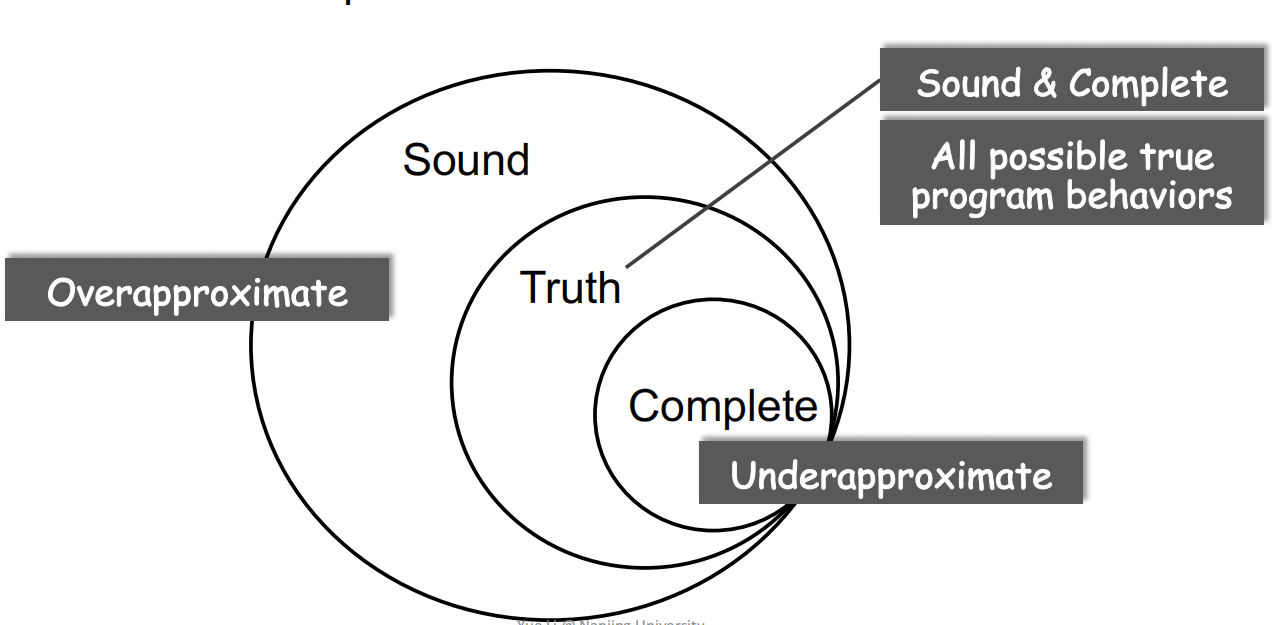
What is Sound and Complete
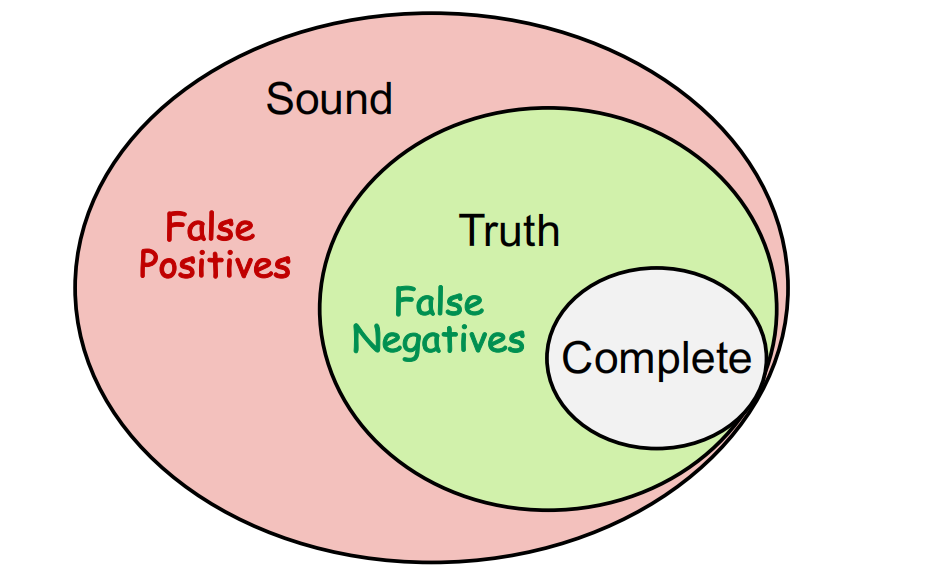
Sound:对于程序存在的可能行为不漏报但有错报Truth:既不错报也不漏报Complete:漏报
false negativesfalse positive
Userful Static Analysis
• Compromise soundness (false negatives)
• Compromise completeness (false positives)
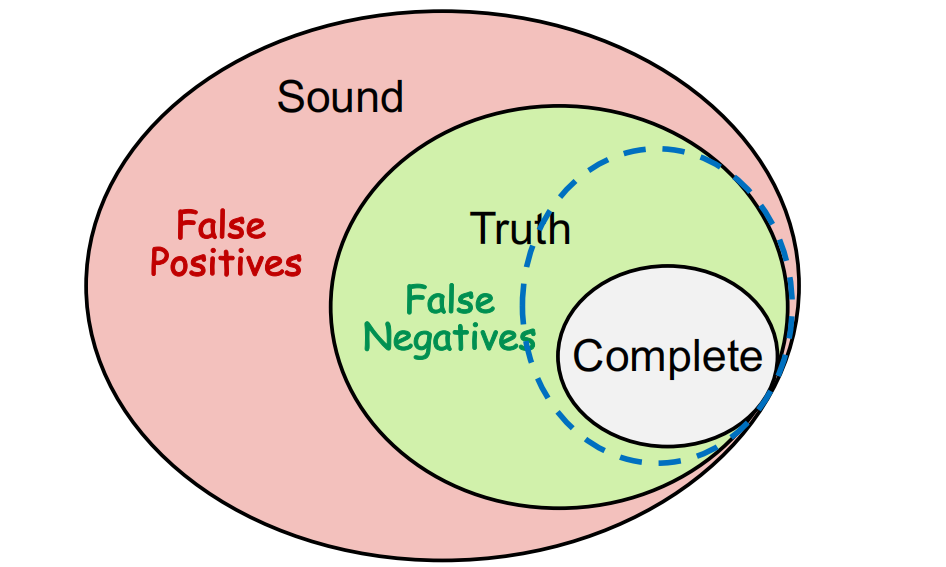
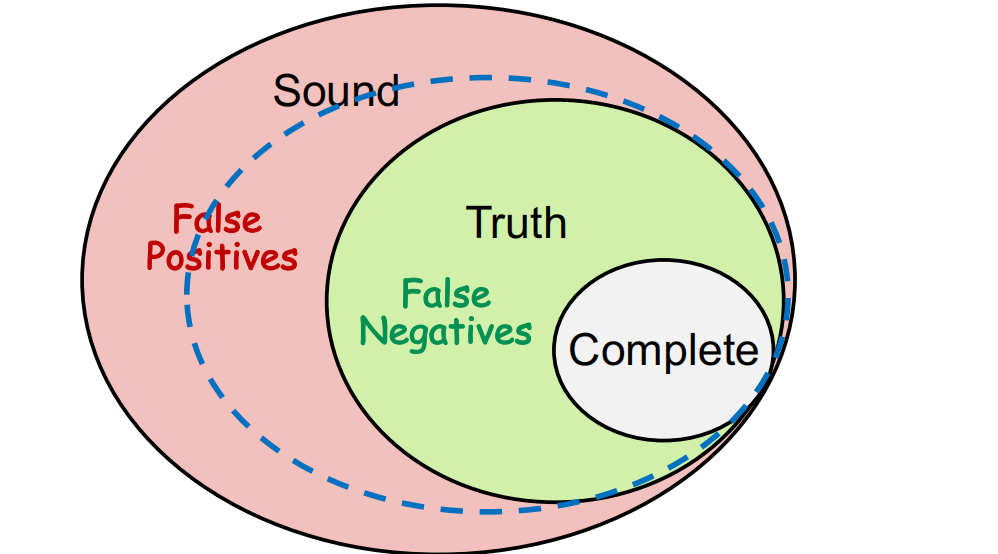
Nowdays, Static Analysis’ trends:
Sound but not fully-precise static analysis
Necessity of Soundness
Soundness mean more bugs could be found
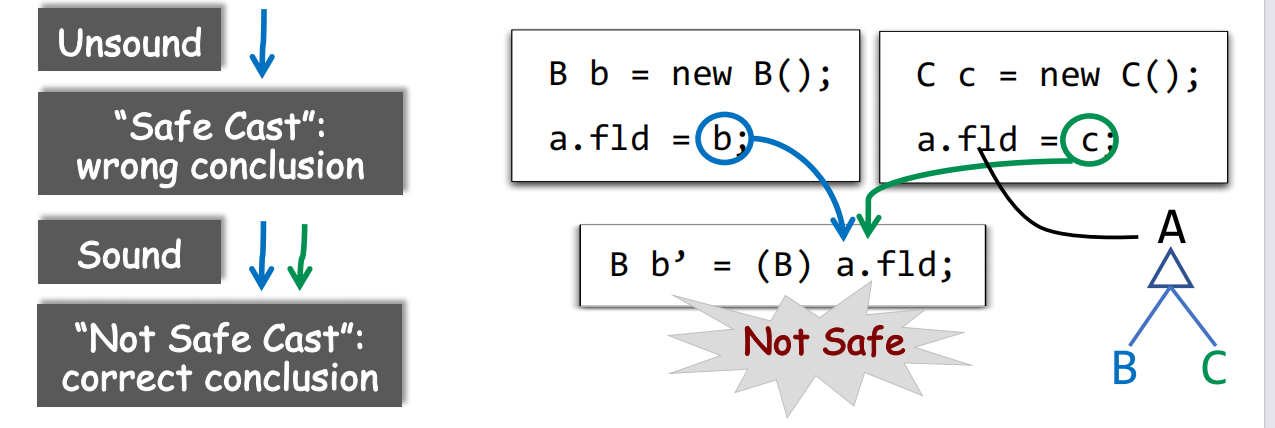
Example of Soundness
1 | if(input) |
Static Analysis Results:
When input is true, x = 1
When input is false, x = 0
=> sound
x = 1 or x = 0
=> sound
x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
=> sound
x = -1, 0
=> unsound
Abstraction
对于变量进行符号抽象
一个形象的例子:
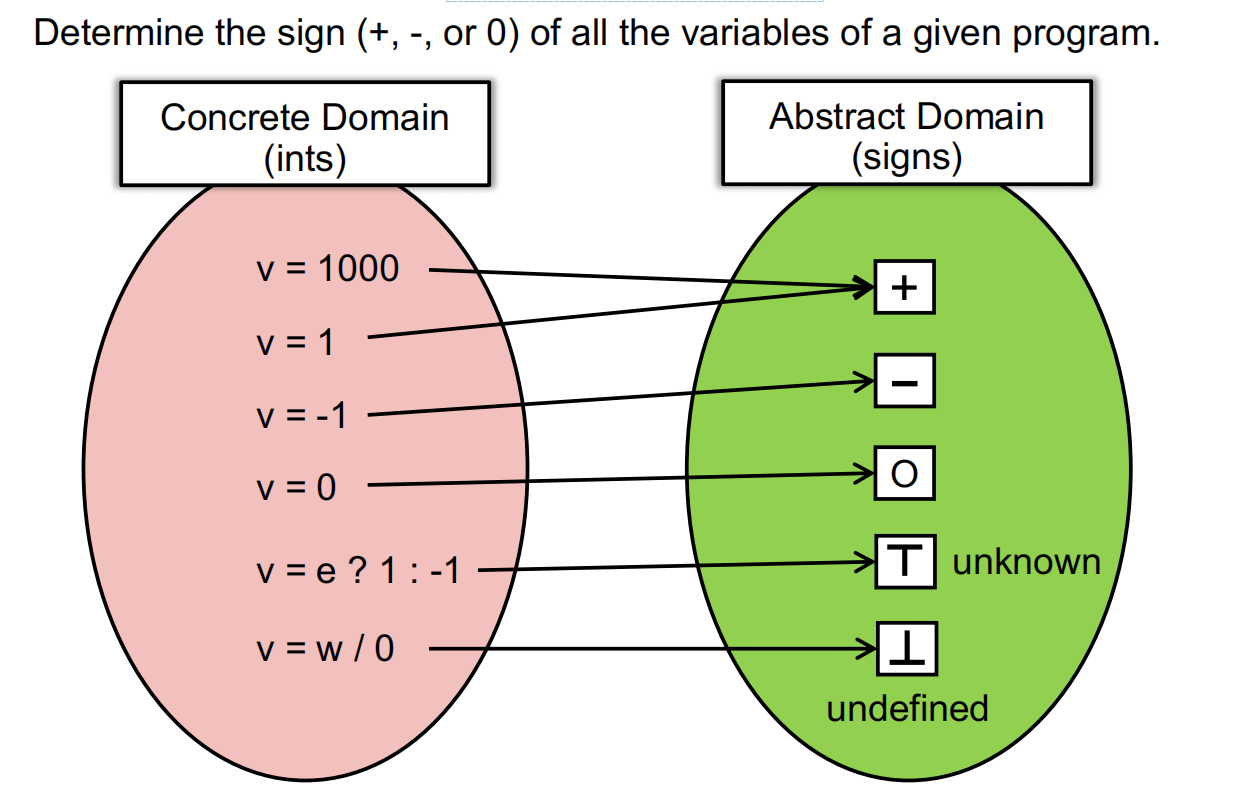
- 定义符号之后,那么可以对运算进行相应的定义了
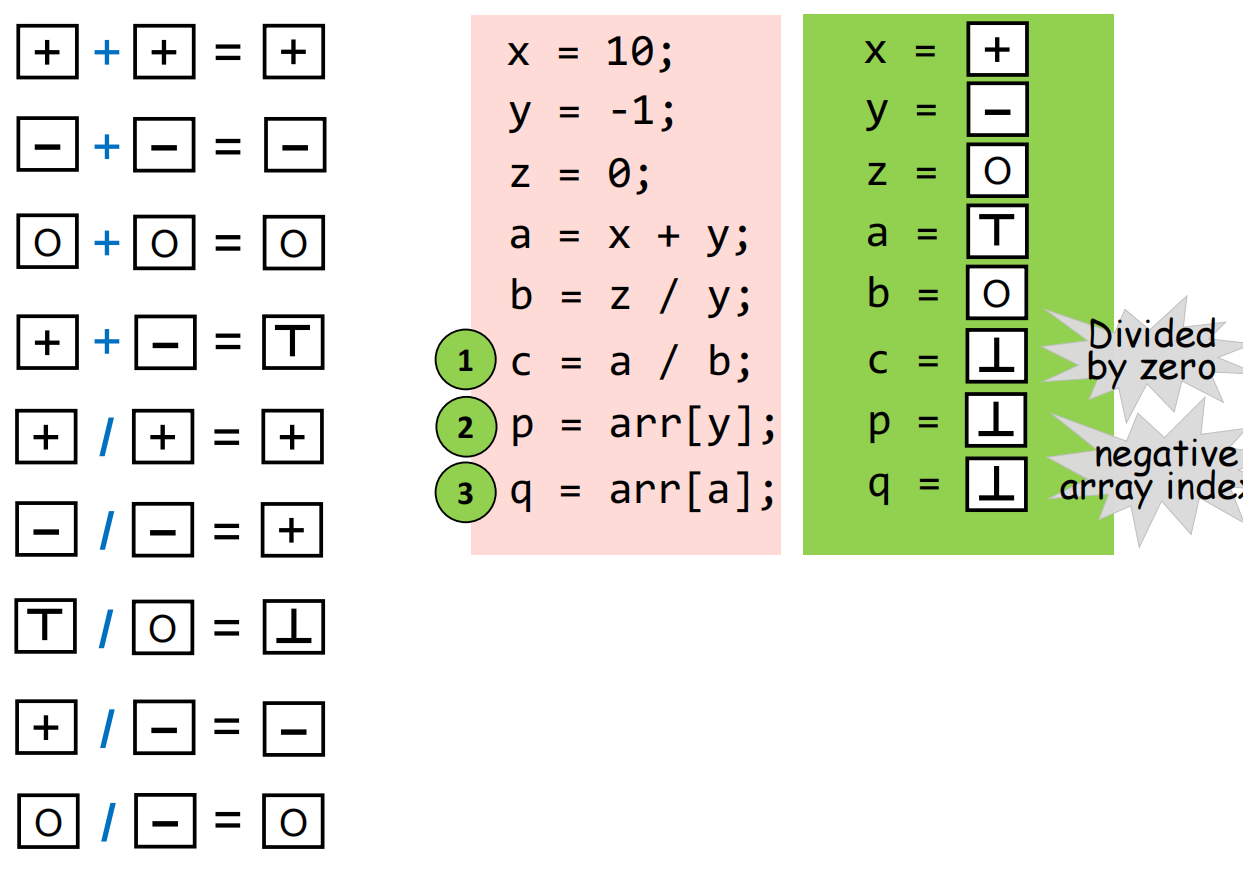
sound:

Over-approximation
Control flow (from wiki) :
control flow is the order in which individual statements, instructions or function calls of an imperative program are executed or evaluated
Control flow Statement(控制流语句)
- 无条件分支或跳转
- 条件分支
- 循环判断分支
- 子例程、协程
- 无条件停止
程序分析中难免会碰到路径爆炸问题
我们通常采用flow merge
来完成Over-approximation
